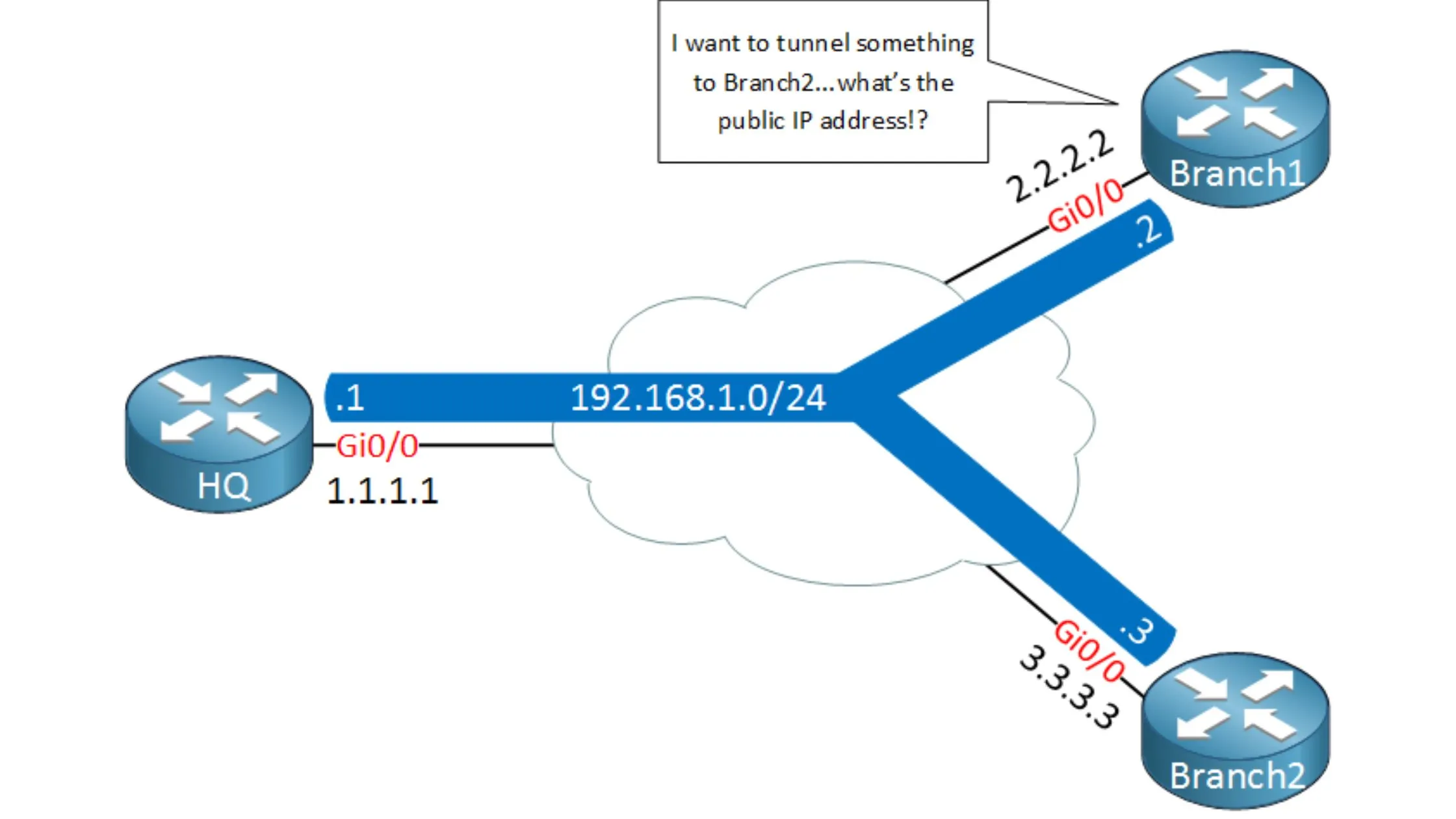
Dynamic Multipoint VPN aka DMVPN is a flexible network solution which enables organizations to establish secure and efficient communication between several sites without the need for static configuration of every device.
DMVPN plays an important part in networking as it is a dynamic and scalable VPN deployment approach. It concerns itself with the difficulties of connecting branch offices to a central site and enables encrypted Wide Area Network (WAN) connectivity. For instance, Cisco’s Dynamic Multipoint Virtual Private Network is considered an ideal solution for organizations that intend to establish cost-effective and protected branch-to-branch connections. By using routing techniques and an overlay architecture Dynamic Multipoint VPN improves scalability, flexibility as well as simplicity of deployment in the network making it a must-have instrument for modern enterprises.
DMVPN’s dynamic nature means that secure connections may be set up and maintained quickly, so it becomes a particularly suitable solution for organizations whose network demands are ever-changing. DMVPN is a valuable asset that can easily adapt to changing network topologies and tie distant sites together in creating resilient, cost-effective enterprise networks.
Benefits of DMVPN
Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) offers several advantages that contribute to its popularity in networking solutions:
- Routing-Based Failover: Dynamic Multipoint VPN enables routing-based failover, ensuring continuous connectivity by seamlessly switching between WAN links. This enhances network reliability and availability.
- Flexibility in Network Design: By using Dynamic Multipoint VPN, organizations can build a VPN network with multiple sites without the need for static configurations on every device. This flexibility simplifies network design and adaptation to changing requirements.
- Cost Reduction: DMVPN offers superior internet speed and reliability, leading to cost reduction in secure communications. Operational expenses are minimized without compromising performance.
- Capital Efficiency: DMVPN provides a capital-efficient solution, eliminating the need for a large initial investment. This is particularly advantageous for organizations with budget constraints.
- Simplified Network Topology: Lower administrative costs are achieved through Dynamic Multipoint VPN’s simplified WAN network topology. Administrators can focus on more critical tasks as DMVPN streamlines network management.
The unique features of DMVPN include operational efficiency, cost savings and the flexibility in design aspect thus it becomes a solution preferred by organizations looking for secure as well as dynamic connectivity across various sites.
DMVPN Components
Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) includes a number of main components that are assembled together to form an active and effective network. These components include:
- Hub: The central point in a Dynamic Multipoint VPN network where spokes connect. The hub facilitates communication between spokes and manages the overall VPN.
- Spoke: Remote sites or branch offices that connect to the hub. Spokes communicate with each other via the hub, forming a dynamic and scalable network.
- Multipoint GRE Tunnels: DMVPN uses Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE) tunnels to establish direct communication between spokes. This allows for efficient data transfer without routing through the hub.
- NHRP (Next Hop Resolution Protocol): NHRP is applied in address resolution, where it maps physical IP addresses to logical tunnel ones. It allows spokes to dynamically learn each other’s public IP addresses.
- mGRE (Multipoint GRE): mGRE is a type of GRE that allows the possibility to have multiple destinations in one tunnel. In Dynamic Multipoint VPN, MGRE enables spokes to communicate directly without the need or having individual point-to-point tunnels.
- IPsec (Internet Protocol Security): DMVPN utilizes IPsec for secure communication over the GRE tunnels. It provides encryption, authentication, and data integrity to protect the transmitted data.
- Routing Protocol: DMVPN supports various routing protocols (e.g., EIGRP, OSPF) for dynamic route exchange between spokes and the hub. This ensures efficient routing and adaptability to network changes.
These components are crucial for designing, deploying, and maintaining a Dynamic Multipoint Virtual Private network. The combination of hub-and-spoke architecture, GRE tunnels, NHRP, mGRE, IPsec, and routing protocols contributes to the flexibility and scalability that Dynamic Multipoint VPN offers.
Design Considerations
Designing a DMVPN solution involves careful planning to achieve the best results in terms of performance, security and compatibility with legacy network infrastructure.
Firstly, setting specific goals is essential. Specify the concrete goals of DMVPN installation, for instance, better connections between remote sites or bigger scalability and improved existing management costs. The configuration process is guided by clear goals that allow it to measure the success of Dynamic Multipoint Virtual Private Network.
The other critical aspect is to select suitable routing techniques. Dynamic Multipoint VPN supports multiple routing protocols like EIGRP and OSPF. It will depend on what network topology the organization has in place currently; scalability needs, and their preference routing protocol. Correctly configuring the routing policy ensures smooth data transmission between Dynamic Multipoint VPN elements.
DMVPN should integrate smoothly with the existing network infrastructure. Evaluate the current network architecture, hardware components and software parts. Implement necessary changes to satisfy DMVPN while ensuring there is synergy in your existing solution.
Tools for monitoring DMVPN performance
To monitor Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN) performance effectively, several tools and techniques are available:
- SolarWinds THWACK Forum Discussion:
- Explore community discussions on THWACK for insights into various methods and tools used by network professionals to monitor Dynamic Multipoint VPN tunnels. Participate in forums for practical experiences and recommendations.
- Cisco DMVPN Tunnel Health Monitoring:
- Leverage Cisco’s Dynamic Multipoint VPN—Tunnel Health Monitoring and Recovery feature. This functionality, based on NHRP (Next Hop Resolution Protocol), controls tunnel interface states according to health conditions, enhancing reliability.
- Network Monitoring Tools:
- Employ network monitoring tools such as SolarWinds Network Performance Monitor (NPM) or other similar solutions. These tools offer comprehensive monitoring, including bandwidth utilization, latency, and device health, aiding in DMVPN performance assessment.
- ResearchGate Study on DMVPN Network Performance:
- Refer to research studies like the one on ResearchGate assessing Dynamic Multipoint Virtual Private Network performance based on dynamic routing protocols and basic IPsec encryption. Gain insights into methodologies and metrics for performance evaluation.
- Reddit Community Recommendation – IP SLA:
- Explore recommendations from the networking community on Reddit, where users suggest using IP SLA (Service Level Agreement) for monitoring spoke-to-spoke connectivity within a DMVPN environment.
These tools and resources offer a combination of real-world experiences, vendor-specific features, and community insights to effectively monitor and optimize DMVPN performance.
Future Trends in DMVPN
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into Dynamic Multipoint VPN solutions is foreseen, enhancing security by intelligently adapting to network threats and optimizing performance based on historical data.
Advancements in quantum computing may prompt the integration of quantum-resistant encryption protocols within Dynamic Multipoint Virtual Private Network implementations, ensuring robust security against emerging cryptographic challenges. The rise of Software-Defined Networking (SDN) and intent-based networking may lead to more flexible and automated Dynamic Multipoint VPN deployments, simplifying management and increasing scalability.